Introduction
The Worldwide Asset eXchange™ (WAX) is the world’s most proven and eco-friendly blockchain for NFTs, video games, and collectibles. WAX has pioneered NFTs and next-gen technologies like Decentralized Finance (DeFi) and Distributed Applications (dApps) to bring forward a new phase in the online creation, buying, and selling of digital and physical assets.
Unlike most real-world assets, NFTs are permanent, immutable, and transferrable, with a wide range of potential use cases. Originally, WAX was designed to serve players and collectors in the world of e-Sports and video games who wanted to trade in-game items, but the platform has since expanded, and along with it, so has its community.
The WAX Blockchain is both high performance and programmable, meaning it is more efficient and green than other blockchains and also very developer-friendly, allowing the creation of ‘smart contracts’ via the dApps, which run on the WAX blockchain network and provide innovative DeFi tools for users and businesses worldwide.
Below, you will find an overview of WAX – where it came from, what you can do with it, and where it might be going.
Who Founded WAX and Why?
WAX was founded by William Quigley and Jonathan Yantis, both successful veterans of internet marketplaces and cryptocurrencies, along with lead designer John Brechisci. Its mission is to build a feeless, frictionless platform for virtual commerce (vCommerce) that bypasses rent-extracting middlemen (e.g. Amazon, eBay, PayPal, etc.). In other words, the big idea is to make it as easy and as cheap as possible for anyone to start trading digitally anywhere in the world.
Before WAX came along, anyone who wanted to set up an independent virtual web store had to outsource their security, infrastructure, fulfillment, and payment processing to different expensive centralized providers. This is hard to maintain and runs the risks of network outages from cyber-attacks on centralized servers, de-platforming, and even censorship.
The founders addressed all these issues through the use of what is called a trustless blockchain. A blockchain is a sort of database where the data is stored in blocks all chained together chronologically in such a way that it is impossible to hack. The WAX blockchain is also distributed over a network of computers which makes it very hard to attack or shut down.
The nature of the blockchain’s basic architecture is that every transaction is transparent and verifiable, meaning a business deal is no longer a faith-based process. Why? Because the WAX blockchain holds a super-accurate, unhackable ledger of everything that has ever happened, such as who sold what to whom, on what date, and according to what exact set of pre-conditions. It is much harder to cheat.
The WAX blockchain needs an algorithm for the validation and management of data and uses one called ‘Delegated Proof of Stake’ (DPoS). This method is much less energy-intensive than the older ‘Proof of Work’ (PoW) competition algorithm as used by the likes of Bitcoin and Ethereum, who are famously energy-hungry and bad for the environment.
This DPoS method of blockchain validation also helps to make the blockchain more ‘scalable’, meaning it is easier to add users and transactions, and it all replaces centralized governance and competition with a staking and cooperation validation system to create a positive feedback loop within the WAX ecosystem.
To achieve the ‘Proof of Stake’, a number of WAX governor ‘guilds’ are chosen on a monthly basis by the votes of the entire WAX community of users, who can all earn WAX Rewards tokens every time they vote.

Many of the WAX guilds are also active developers on the WAX blockchain, contributing innovative dApps and ‘microservices’ such as the AtomicHub’s NFT Creator and Explorer, which all make it really easy for users to set up an account and begin creating and trading their NFTs.
What Does WAX Do?
Let’s have a quick look at what happens ‘under the hood’ on WAX.
NFTs
The basic element on WAX is the NFT. Users can trade these ‘assets’ securely around the world without paying high intermediary fees (e.g. eBay takes 12.8%) or “gas fees” as with other blockchain-based trading systems (e.g. ones based on Ethereum).

The basic element on WAX is the NFT which is essentially a digital token of any sort of digital file – typically an image, audio, video. On WAX, users can trade their ‘assets’ securely around the world without paying high intermediary fees (e.g. eBay takes 12.8%) or wildly fluctuating “gas fees”, which can get very expensive indeed depending on the time of day or year (e.g. Ethereum-based trading systems).
WAX is also a great deal more flexible than other NFT platforms due to constant developments by programmers and coders, who use a ‘protocol’ based around open standards such as AtomicAssets. This means WAX benefits from the creative input of a lot of different people with different ideas. For example, even the most simple NFT on WAX can have multiple owners/collaborators so that every time there is a secondary sale (e.g. in a secondary marketplace), all the originators of the NFT can automatically get their percentage.
This ability to share revenue between originators opens up entirely new models for the licensing of digital content. This in turn may also fundamentally reconfigure reward and value as fans and creators connect to each other directly, without any blockages, censorship, or commercial constraints on their work. The process of so-called digital ‘disintermediation’ has been talked about since the early 1990s but this degree of seamless peer-to-peer trading has been impossible until now.
WAX makes this type of worldwide connectivity a viable reality in everyday business processes.
dApps
Another central feature of WAX is its Distributed Applications (dApps). These are pieces of software that run on the WAX blockchain network. They mostly have a simple front-end interface for the users and a back-end for a ‘smart contract’, pieces of code that perform complex background tasks.
You can use ready-made dApps that help you work in WAX or if you have coding skills (e.g. in C++ etc.), you can also easily program your own using a ‘mix and match’ approach because of the high ‘composability’ of the WAX platform. WAX is a bit like Lego™ and – unlike closed systems – it is specifically designed to interoperate and work with other dApps from other blockchains and NFTs from other marketplaces.
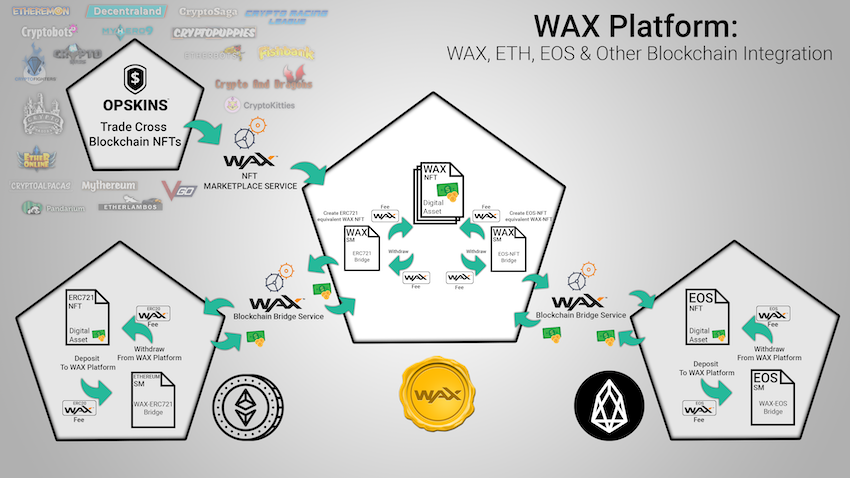
Up till now, most dApps on WAX have been designed for trading video game ‘collectibles’, but there is a wide potential for trading dApps in other areas. One interesting new dApp is WAX’s own vIRL(™), which can ‘tokenize’ a real physical object (e.g. a one-off 12” vinyl music dubplate), and link it to an online virtual token (NFT), such that both can be owned and traded. And NFTs aren’t limited to art either. The possibilities are endless: fractional ownership of property (real estate) and decentralized loans being just two examples.
To get the bigger picture of how potentially radical dApps are, just consider how people paid for and traded goods 50 years ago before online payment systems like banks and credit cards became so central to our lives. Blockchain provides a new, secure solution that is radically different from the old centralized model because it is both verifiable and transparent – it is ‘trustless’.
Security
Not a day goes by without news of hyper-centralized servers being phished or taken over, or of massive data leaks, DDoS, and ransomware attacks. In the case of a DDoS (Denial of Service), an ‘attacker’ uses a number of distributed devices to attack the Target Victim.
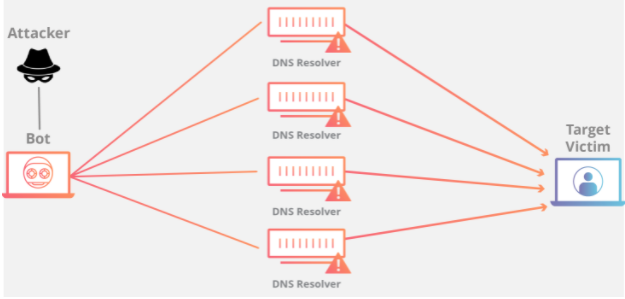
Attacks are only made possible because of the basic architecture of a centralized server. In comparison, a blockchain-based service at its very core is not only secured with state-of-the-art cryptography but also has near-zero downtime because the network has no central point open to such attacks. Of course, security is an ever-evolving field, and WAX, via collaborations with top specialists, provides tools for developers to constantly improve user experience and security.
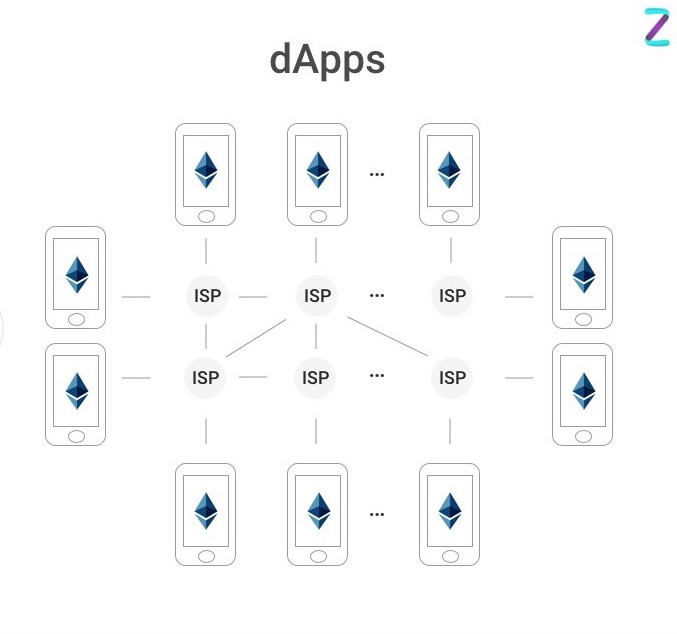
Transactions made by a dApp are automatic and the result cannot be retroactively changed or tampered with. This presents an obvious advantage: if all transaction information is verifiable and immutable, then the risk presented by bad actors is also mitigated. All dApps are essentially ‘open-source’, meaning the code can be reviewed by anyone, and therefore the chance of hidden malware is also minimized.
Arguably, this degree of transparency can lead to a much fairer business environment with fewer resources wasted on fighting crime and expensive entanglements in the courts or arbitration.
Even if there is bad coding or misuse in a dApp, the main blockchain network remains unaffected because every dApp runs ‘isolated’ from the main network. In short, dApps on a blockchain can provide a more transparent, energy-efficient, and dynamic way of servicing a range of different needs in our increasingly digitized world. WAX is ready for this eventuality.
Governance
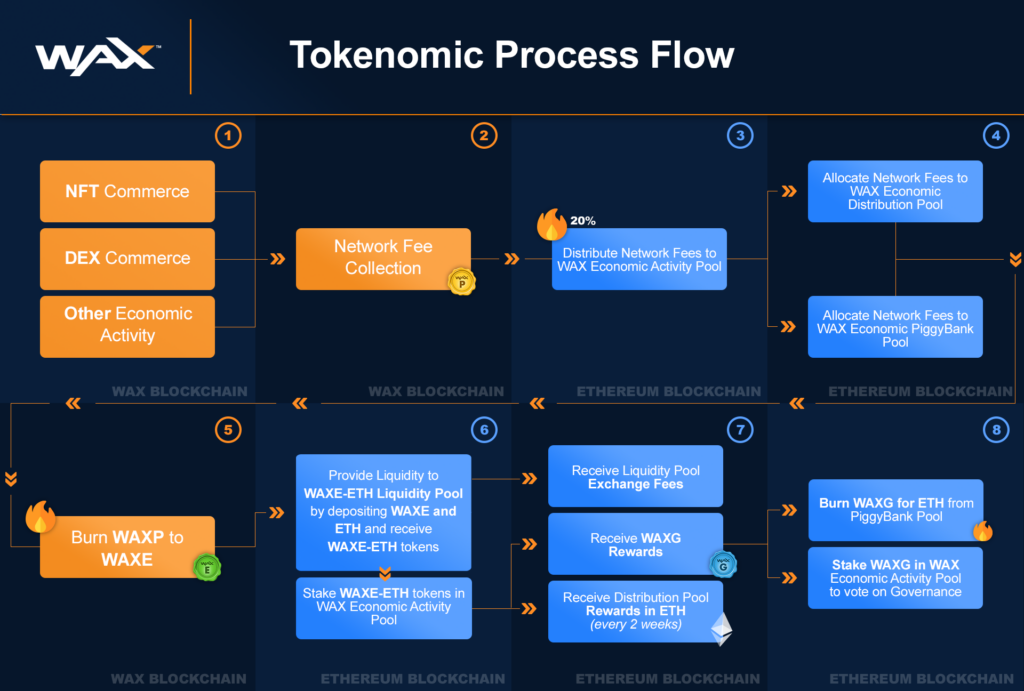
As mentioned above, WAX delegates its block production to a network of 57 ‘guilds’ with an Office of the Inspector General (OIG) elected to evaluate performance, from which the top 21 guilds are graded on a monthly basis. WAX has developed a finely balanced interlocking system of incentives, checks, and balances based on the various types of WAX coins, including WAX reward tokens. This is what is called the WAX ‘tokenomics’ ecosystem, which depends on the active votes, involvement, and inclusion of all WAX users in the management and maintenance of the blockchain.
How can I get involved?
To get started on WAX, you can read this step-by-step article.
It shows you how to sign up for a WAX account. The easiest way to do this is via a ‘managed’ wallet such as a WAX Cloud wallet (WCW) that helps you through the whole process. Using a WCW you can even sign in using your own social media login, which is super convenient (though less secure if you get careless with your password). You can also have an ‘unmanaged’ wallet, such as Scatter, which is more secure but requires more effort on your part. There are even some USB-stick ‘hardware’ wallets for a super-secure solution, such as Ledger.
Once your wallet is in place, you load up with WAXP tokens which can be bought via a credit card or a crypto exchange. If you want to buy NFTs you can read this step-by-step article.
One of the WAX Guilds – pink.gg – has built a suite of very powerful but convenient ‘microservices’ on its AtomicHub which seamlessly integrates with the Wax Cloud Wallet (WCW).
On the AtomicHub, you can browse NFTs with the AtomicHub Explorer engine, or use the NFT Creator to ‘mint’ your own NFT. You can start trading peer-to-peer which is totally free (i.e. transactions are “feeless”). You pay only minimal fees to cover WAX’s three basic processing overheads for transactions (called RAM, NET, CPU). It is also free to create a listing on the main Atomic Hub Marketplace – though every sale takes a 2% ‘blockchain fee’ and 2% ‘marketplace fee’ – which is considerably less than any other equivalent NFT trading options.
Where is Wax Going?
The W.A.S.P. Strategy
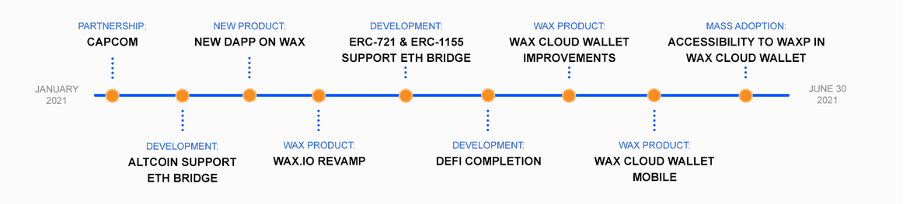
Looking back to 2019, WAX set forth a strategy called “W.A.S.P.”. With over 6+ million accounts by the middle of 2021, the WAX Blockchain has seen a massive explosion in the quantity and value of NFTs traded and has set up a ‘decentralized marketplace’ (e.g. to match Amazon) and a WAX ‘virtual item trading and generation’ platform (e.g. to match Steam). Lastly, the WAX ‘decentralized wallets’ (e.g. to match PayPal) are all up and running.
Everything planned in 2019 has been achieved and more, and WAX is moving further ahead with a roadmap for new dApps, products, and partners.
The Future is Now
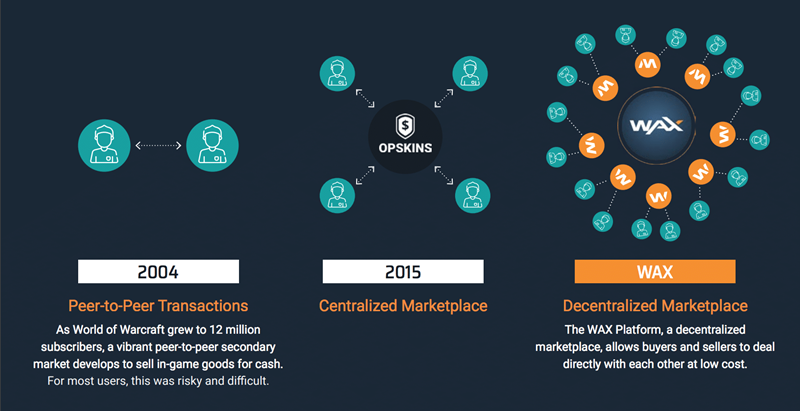
As fans and creators find new ways to interact, the traditional model of trading relationships will either have to adapt or slowly become defunct. Only 20 years ago, massively centralized businesses like Amazon, eBay, and PayPal transformed the way we all buy goods. On the one hand, we can see antitrust pressures and global tension between trading blocs. On the other hand, we see an overall global trend towards peer-to-peer models for devolved marketplaces. For these reasons, WAX and dApps are well-placed to continue this global revolution and extend it into virtual entertainment, art, and collectibles businesses.
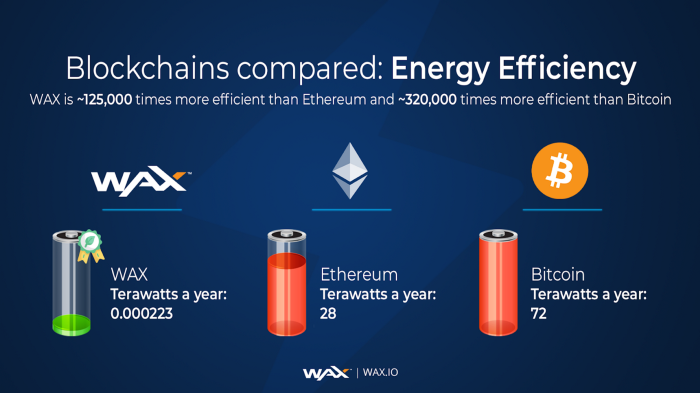
Last but not least – it is important to point out that the WAX model can handle twice the transaction throughput as VISA and it also consumes 125,000 times less energy than its nearest equivalent Ethereum and 320,000 less energy than BitCoin.
Conclusion
WAX hopes to bring a new era of decentralized technologies into all aspects of everyday business. Via Tokenomics, everyone can benefit from the healthy development of WAX and earn WAX rewards tokens. WAX Developers have access to all the tools they need to create new, innovative dApps that will pull technology away from old centralized models towards new distributed models, which are both fairer and greener.
Hopefully, you now know a little more about NFTs, how dApps are used, and the WAX governance model. From here, why don’t you read more of these articles about opening a WAX account or setting up a secure WAX Cloud wallet? There, you can stock up on WAXP tokens, search the marketplace, and start trading or even minting your own Collection of NFTs.



